We are often asked by beginners: what is a domain name and how do domains work? If you are a beginner, then you may have heard that you need a domain to make a website.
However, many beginners confuse domain name with a website or website hosting service. If you are just starting out, then all these different terms may sound too technical.
In this beginner’s guide, we will answer what is a domain name and how domains work. The goal is to help you understand and choose the right domain name for your website.

Here is a quick overview of the topics we will cover in this guide.
- What is a domain name?
- How domains work?
- How is domain name different from website and web hosting?
- Different types of domain names
- Who is responsible for the domain name system?
- How to choose a domain name
- How to buy a domain name
- Frequently asked questions about domain names
What is a Domain Name?
Domain name is the address of your website that people type in the browser URL bar to visit your website.
In simple terms, if your website was a house, then your domain name will be its address.
A more detailed explanation:
The Internet is a giant network of computers connected to each other through a global network of cables. Each computer on this network can communicate with other computers.
To identify them, each computer is assigned an IP address. It is a series of numbers that identify a particular computer on the internet. A typical IP address looks like this:
66.249.66.1
Now an IP address like this is quite difficult to remember. Imagine if you had to use such numbers to visit your favorite websites.
Domain names were invented to solve this problem.
Now if you want to visit a website, then you don’t need to enter a long string of numbers. Instead, you can visit it by typing an easy to remember domain name in your browser’s address bar. For example, wpbeginner.com.
How Domain Names Actually Work?
To understand how domain names actually work, we will take a look at what happens when you enter it in your browser.
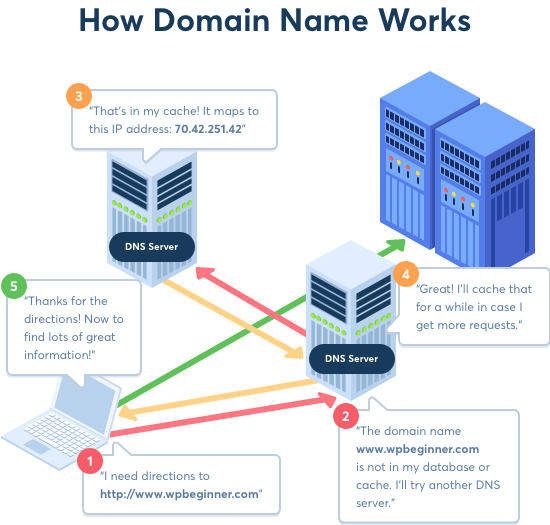
When you enter a domain name in your web browser, it first sends a request to a global network of servers that form the Domain Name System (DNS).
These servers then look up for the name servers associated with the domain and forward the request to those name servers.
For example, if your website is hosted on Bluehost, then its name server information will be like this:
ns1.bluehost.comns2.bluehost.com
These name servers are computers managed by your hosting company. Your hosting company will forward your request to the computer where your website is stored.
This computer is called a web server. It has special software installed (Apache, Nginx are two popular web server software). The web server now fetches the web page and pieces of information associated with it.
Finally, it then sends this data back to the browser.
How is Domain Name Different from a Website and Web Hosting?

A website is made up of files like HTML pages, website builder software, images, and more.
If the domain name is the web address of your website, then web hosting is the home where your website lives.
This is the actual computer where your website’s files are stored. Such computers are called servers and they are offered as a service by hosting companies.
To create your website, you need both domain name and web hosting.
However, it’s important to remember that they are two separate services, and you can buy them from two different companies.
Now you may be wondering, how would it work if you bought them from two separate companies?
You just need to edit your domain name settings and enter the Name Server information provided by your hosting company. Name Server information defines where to send user requests for your domain name.
We recommend getting both your domain name and hosting from the same company. This allows you to easily manage them under the same account.
For more details, see our guide on the difference between domain name and web hosting.
Different Types of Domain Names
Domain names are available in many different extensions. The most popular one is .com. There are many other options like .org, .net, .tv, .info, .io, and more. However we always recommend using .com domain extension.
Let’s take a more detailed look at different types of domain names available.
Top Level Domain – TLD
Top level domain or TLD are generic domain extensions that are listed at the highest level in the domain name system.
There are hundreds of TLDs, but the most popular ones are .com, .org, and .net. Other TLDs are lesser known and we don’t recommend using them. For example, .biz, .club, .info, .agency, and many more.
Country Code Top Level Domain – ccTLD
Country code top-level domain or ccTLD are country specific domain names which end with country code extension like .uk for the United Kingdom, .de for Germany, .in for India.
They are used by websites that want to target audiences in a specific country.
Sponsored Top Level Domain – sTLD
Sponsored top-level domain or sTLD is a category of TLDs that has a sponsor representing a specific community served by the domain extension.
For example, .edu for education-related organizations, .gov for the United States government, .mil for the United States military, and more.
Who is Responsible for Domain Name System?
Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) manages the domain names system. It is a non-profit organization that creates and implements the policies for domain names.
ICANN gives permission to companies called Domain Name Registrars for selling domain names. These domain registrars are allowed to make changes to domain names registry on your behalf.
Domain name registrars can sell domain names, manage its records, renewals, and transfers to other registrars.
As a domain name owner, you are responsible for telling the registrar where to send requests. You are also responsible for renewing your domain registration.
How to Choose a Domain Name for Your Website?

There are currently more than 350 Million registered domain names and thousands more get registered each day.
This means that all the good ones are already registered or will be registered very soon. This puts a lot of pressure on new users to come up with a domain idea for their website.
We’ve created a free AI-powered business name generator tool that helps you come up with creative company name ideas and check domain name availability status to help you save time.
Here are some quick tips to help you choose a domain name for your next website.
- Stick with a .com domain name as it is the most popular, easy to remember, and easy promote.
- Make sure it is shorter and easy to remember
- Make it easy to pronounce and spell
- Do not use numbers or hyphens
- Use domain name generators to come up with clever domain name ideas
For more tips and practical advice, see our guide on how to choose the best domain name for your website.
How to Buy a Domain Name?
You can buy domain names from one of the many domain name registrars. A domain name typically costs 14.99 per year. Some popular domain name companies are:
- Domain.com
- Network Solutions.
- GoDaddy
However, buying a domain does not automatically give you hosting service. For that, you will need a website hosting account as well.
Many WordPress hosting companies offer domain registration services as well. This allows you to manage both services under one account, and you also don’t need to worry about changing name server settings for your domain.
We recommend using Bluehost. They are offering WPBeginner users a free domain name and 60% discount on hosting. Basically you can get started for $2.75/month.
Frequently Asked Questions About Domain Names
Over the years we have helped thousands of beginners start their first websites. We have heard almost every possible question about domain names that you can think of.
Following are the answers to some of the most commonly asked questions about domain names.
1. What is a subdomain?
A subdomain is basically a child domain under the main domain name. For example, videos.wpbeginner.com is a subdomain of wpbeginner.com.
Once you register a domain, you have the permission to create subdomains for it by yourself.
Subdomains are commonly used by websites to create child-sites under the same domain name. For example, a business website can create a subdomain for their blog or their online store as store.example.com or blog.example.com
2. Can I cancel my registration of a domain name?
Some domain registrars allow you to cancel your domain registration at any time. If you cancel your registration, it will become available for others to register.
Other domain name registrars allow you to simply let your domain registration expire.
In most cases, you will not get any refund for the domain registration. However, some domain registrars do have refund policies which you may want to discuss with them before canceling your registration.
If you don’t have the auto-renew feature turned on, then your domain name will simply expire after the registration period you have paid for.
3. Can I move my website to a different domain name?
Yes, you can. You can point your domain name to your hosting server. You can also keep both domain names pointing to the same website.
However, search engines consider it duplicate content and that will affect your search rankings.
We have a step by step guide on how to properly move a website to new domain name and setup redirects, so you don’t hurt your SEO.
4. Can I sell a domain name?
Yes, you can sell your domain name. Domain names are like real estate for web. There is a huge demand for good brandable custom domain names.
Trading domain names is a multi-million dollar industry. Since domain names are so cheap, smart entrepreneurs are always looking for great domain name ideas to get their hands own.
If you want to sell your domain name, then there are many marketplace websites like Sedo, GoDaddy, and others where you can list your domain for sale.
Popular registrars like Domain.com and Network Solutions also let you buy premium domains right from their domain search feature.
Related: See the best GoDaddy alternatives for buying domains.
5. What is domain privacy? Do I need it?
ICANN requires people registering domain names to provide an email, physical address, phone number, and other personal information to be made available publicly.
Domain Privacy is a separate add-on service sold by domain registrars. It allows you to show proxy information instead of your actual personal info.
You don’t need to buy domain privacy if you don’t want to. However if you are concerned about privacy, then you can buy this service for a small cost.
6. Can I buy more than one domain name?
Yes, you can buy as many domain names as you like.

